Compare three industrial heat exchangers having the same exchange
Surface area and different technologies
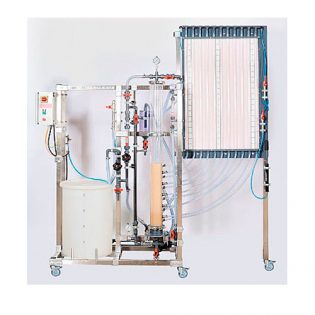
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
- Heating unit, for hot water production with temperature controller, and safety thermostat.
- Selection of cold water flow, set of two three way valves & sets of valves to select the exchanger.
- High pressure relief valve, loaded at 3 bars.
- Single-tube glass / SS exchanger EXCH1: Glass shell.
- Multi tubular exchanger ECH2: stainless steel tubes, . Glass shell and SS baffle-plates.
- Plate heat exchanger ECH3: Welded stainless steel plates.
Instrumentation
- Temperature probes Pt100Ω.
- Flowmeters.
Dim : 190 x 80 x 198 cm – 200 kg
SS tubular framework 40 x 40mm
Heat exchanger
A heat exchanger is a device used to transfer heat between a solid object and a
fluid, or between two or more fluids. The fluids may be separated by a solid
wall to prevent mixing or they may be in direct contact. They are widely used in
space heating, refrigeration, air conditioning, power stations, chemical plants,
petrochemical plants, petroleum refineries, natural-gas processing, and sewage
treatment. The classic example of a heat exchanger is found in an internal combustion
engine in which a circulating fluid known as engine coolant flows through radiator coils
and air flows past the coils, which cools the coolant and heats the incoming air.
Compare the three technologies
Single-tube glass/stainless steel heat exchanger
Shell-and-tube heat exchanger with glass shell and stainless steel tubes
SS plate-type heat exchanger
Determine the influence of flow regimes on heat transfer
Turbulent and laminar regimes
Co-current and counter-current circulation
Study of temperature gradient (optional).
Characterization of heat transfers
Thermal balance
Yield
Overall experimental and theoretical heat exchange coefficient K




















 PIGNAT et ses partenaires utilisent des Cookies strictement nécessaires, de navigation et marketing et publicitaires. Pour plus d'informations, consultez notre “politique de cookies". Acceptez le dépôt de tous nos cookies en cliquant sur "J'accepte" ou sélectionnez les catégories de cookies déposés en cliquant sur "Voir les préférences” sinon refusez nos cookies non strictement nécessaire en cliquant sur "Je refuse”.
PIGNAT et ses partenaires utilisent des Cookies strictement nécessaires, de navigation et marketing et publicitaires. Pour plus d'informations, consultez notre “politique de cookies". Acceptez le dépôt de tous nos cookies en cliquant sur "J'accepte" ou sélectionnez les catégories de cookies déposés en cliquant sur "Voir les préférences” sinon refusez nos cookies non strictement nécessaire en cliquant sur "Je refuse”.