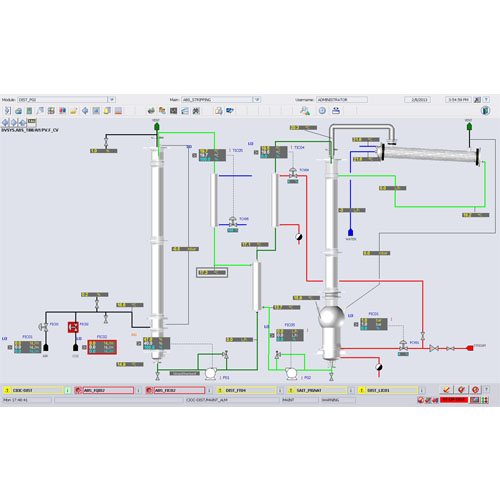
Understand the continuous absorption process
OTP pilots allows work on an industrial scale in various fields:
chemical engineering, maintenance, supervision
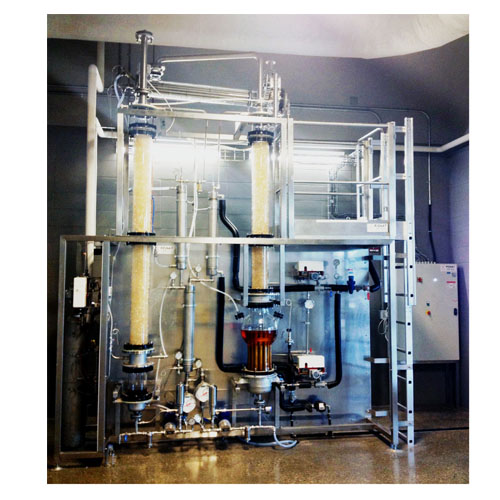
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
Absorption:
- SS gear pump.
- SS heat exchanger (cooler).
- Two section of glass column. Packing: Raschig rings in glass.
- Cool exchanger line allows to cool the solvent.
Regeneration:
- Two section of glass regeneration column. Packing: Rashig rings in glass.
- Glass exchanger shell, SS tube, system reflux.
- A SS heat Exchanger, with steam pneumatic control valve.
- Thermosiphon reboiler with glass shell and a SS tube heat exchanger heated by steam.
Instrumentation
- 12 temperature probes Pt100Ω.
- 2 air mass flow transmitters.
- 1 water cooling transmitter.
- 3 flow transmitter ( supply, and low absorption
and regeneration columns). - Differential pressure transmitter.
- Rate control.
- Absorption level transmitter.
- Vapor/regeneration pressure transmitter.
- 2 CO2 transmitter analyzers.
Dim : 290 x 100 x 390cm – 1000 kg
SS tubular framework 40 x 40mm
Absorption and regeneration
The solute migration phenomenon from the gas to the liquid phase occurs when both phases are contacted in the packing
of the reverse flow absorption column. This highlights the absorption operation (solvent purification).
The regeneration phenomenon is observed on the second column, which is continuously fed.
An energy‐saving heat exchanger is placed between the two columns to optimize the power spent on the unit.
A second heat exchanger is placed on the absorption side to cool the fluid returning to the head of the column.
The third heat exchanger, placed on the regeneration side, allows the solution to be heated in order to be regenerated in column 2.
The use of such a unit allows one to remove CO2 from air using monoethanol amine and to recover pure CO2 to capture it.
Study of the transitional phases
Starting the unit
Put equilibrium conditions
Stop the unit
Research of the optimum operating parameters
Feed rate, preheating temperature, reflux rate, column pressure losses
Study of the effectiveness of the process
Mass balance, thermal balance, yield, productivity
Study of the technologies implemented





















 PIGNAT et ses partenaires utilisent des Cookies strictement nécessaires, de navigation et marketing et publicitaires. Pour plus d'informations, consultez notre “politique de cookies". Acceptez le dépôt de tous nos cookies en cliquant sur "J'accepte" ou sélectionnez les catégories de cookies déposés en cliquant sur "Voir les préférences” sinon refusez nos cookies non strictement nécessaire en cliquant sur "Je refuse”.
PIGNAT et ses partenaires utilisent des Cookies strictement nécessaires, de navigation et marketing et publicitaires. Pour plus d'informations, consultez notre “politique de cookies". Acceptez le dépôt de tous nos cookies en cliquant sur "J'accepte" ou sélectionnez les catégories de cookies déposés en cliquant sur "Voir les préférences” sinon refusez nos cookies non strictement nécessaire en cliquant sur "Je refuse”.